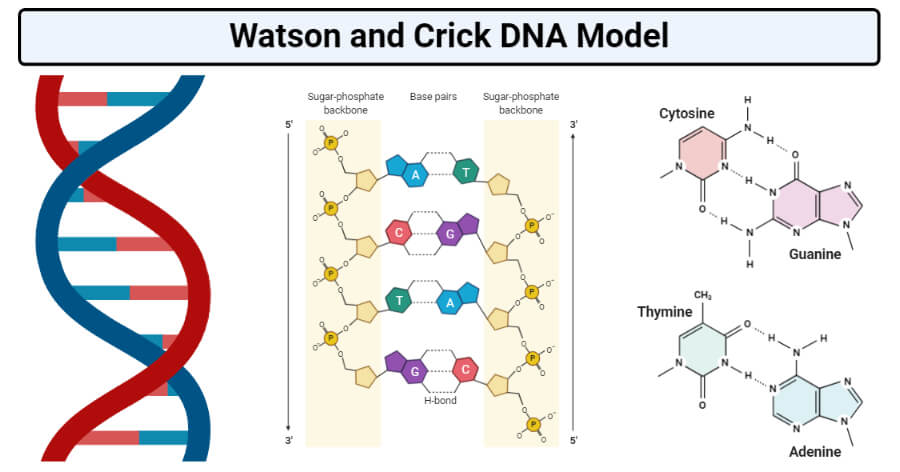
Nucleic acids DNA and RNA structure LIKE US ON FACEBOOK https//fbme/MedsimplifiedNucleic acids are biopolymers, or small biomolecules, essential to all kThe structures of many tRNA molecules are known in quite detail These are comparatively very small with a molecular weight of about Basic structure of all tRNA molecules is on the clover leaf pattern Clover leaf model of tRNA is given in Fig 917 tRNAs are found in cytoplasm and consist of only about 80 bases The WatsonCrick DNA Double Helical Structure In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick deduced the threedimensional structure of DNA The essential functions of their model of DNA are as follows Two helical polynucleotide chains are coiled around a common axis The chains run in opposite directions (antiparallel)
What Are The Structure Of Rna And Dna And How One Might Be Used To Create The Other Socratic
Model of dna and rna structure
Model of dna and rna structure-RNA does, in contrast to DNA, form short double strand structures on itself, thereby forming so called stem and loop structures Both DNA/RNA double helices and RNA/RNA double strands have an ADNA like conformation, also called ARNA or RNARNA AND ITS STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND TYPES With the discovery of the molecular structure of the DNA double helix in 1953, researchers turned to the structure of ribonucleic acid (RNA) as the next critical puzzle to be solved on the road
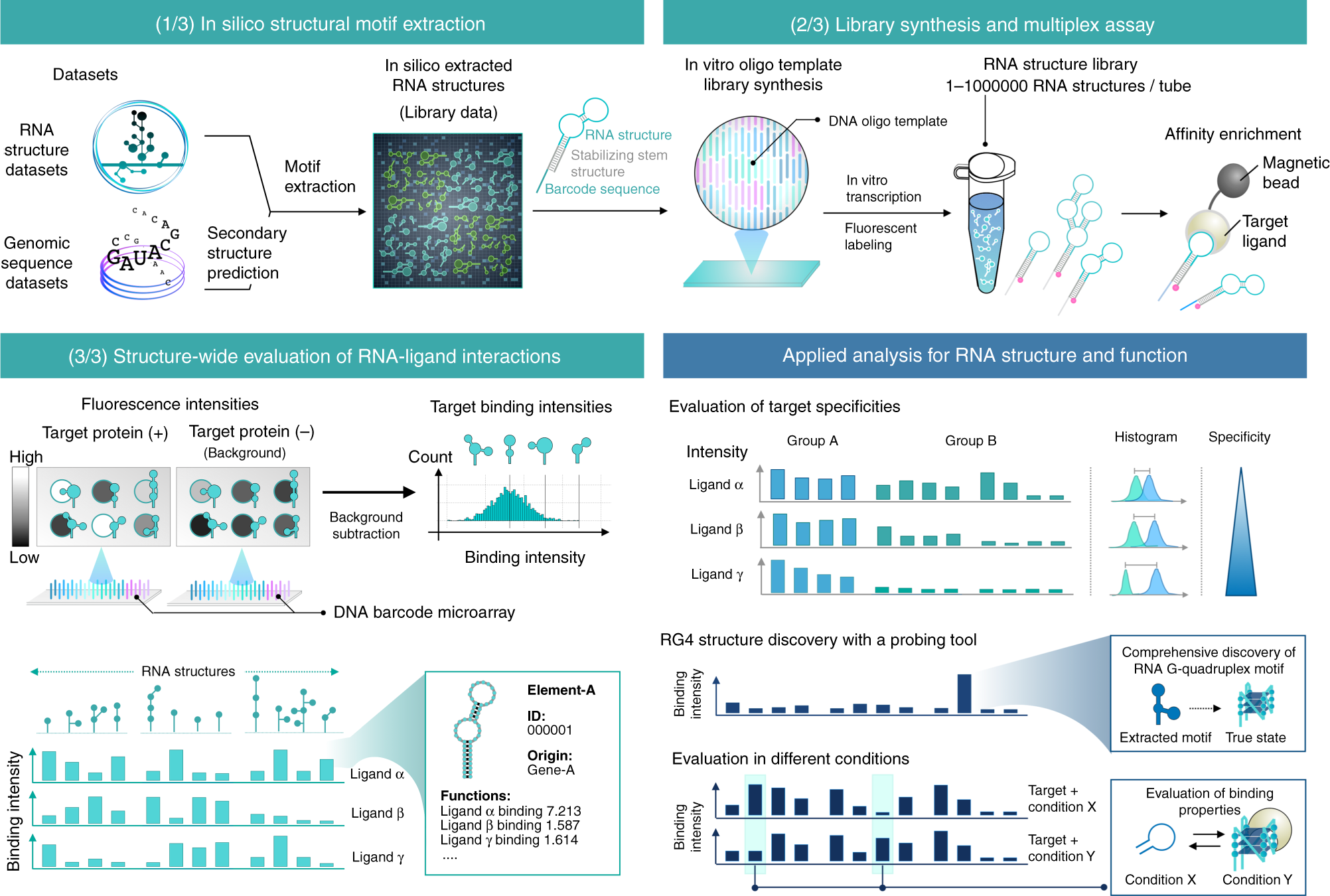



Rna Structure Wide Discovery Of Functional Interactions With Multiplexed Rna Motif Library Nature Communications
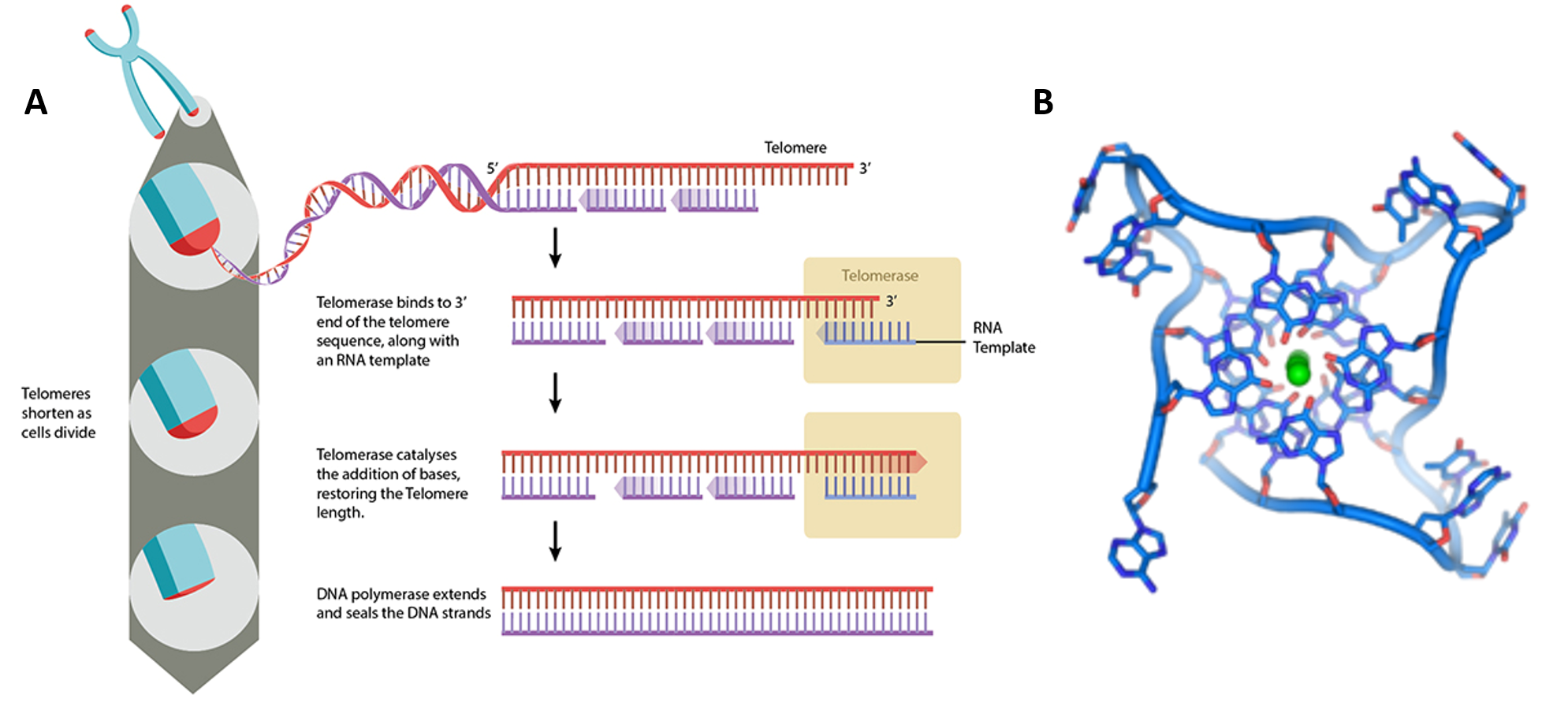
The detailed structural features and functions of the telomeric RNA at human chromosome ends remain unclear, although this RNA molecule may be a key component of the telomere machinery In this study, using model human telomeric DNA and RNA sequences, we demonstrated that human telomeric RNA and DNA oligonucleotides form a DNARNA GquadruplexDNA Structure Watson and Crick's model of DNA The structure of DNA was a mystery before the 1950s It was at the beginning of 1950s, James Watson (American biologist) and Francis Crick (British physicist) after combining the available physical and chemical data and based on their research introduced the doublehelix model for DNAThe work of Rosalind Franklin and Maurice The choices include five modelbuilding types (i) customized singlestranded RNA or doublehelical DNA structures with userspecific base sequences and rigidbody parameters (Supplemental Data S2);
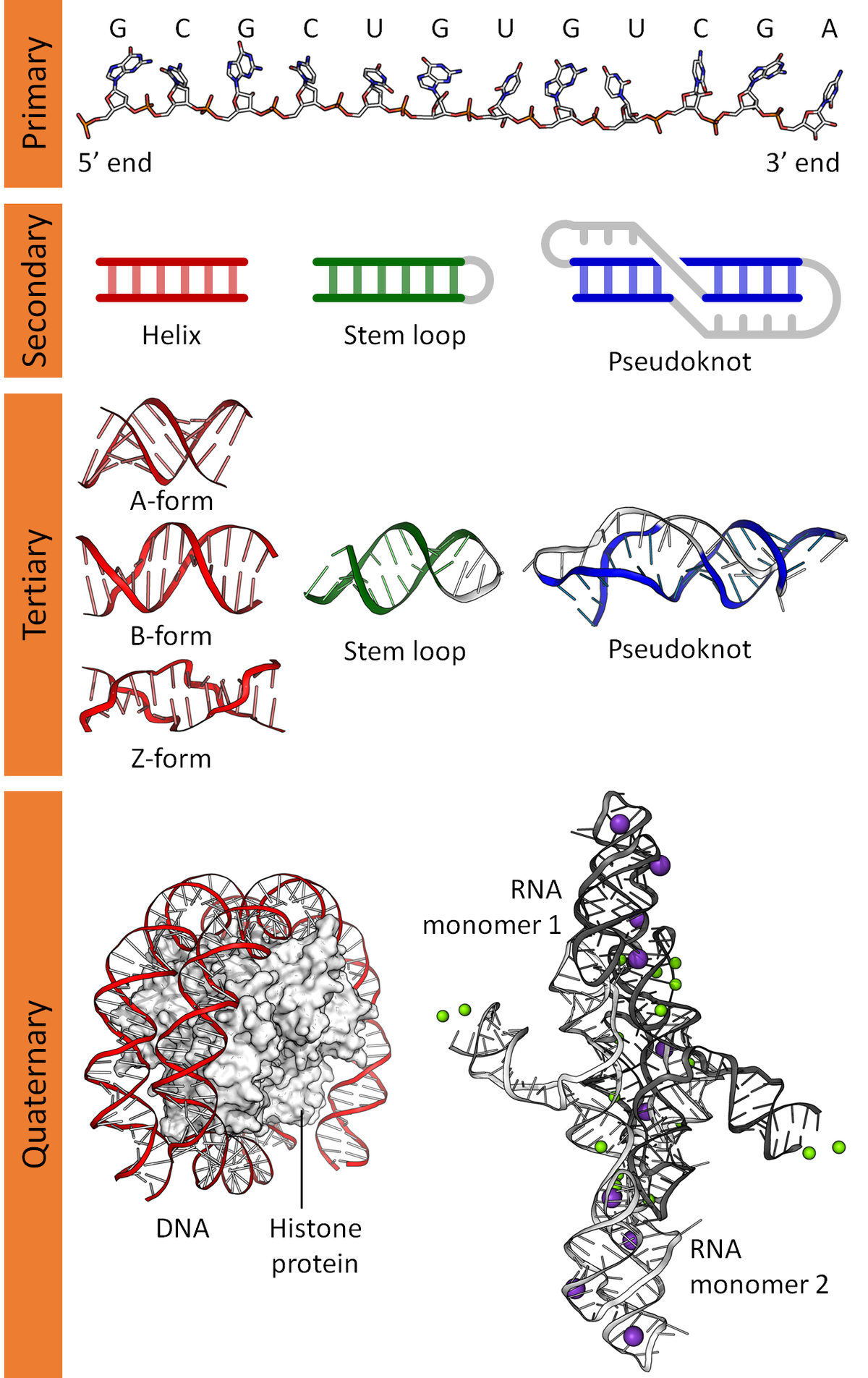
RNA and DNA Nucleic acids are critical regulators of cellular functions across all domains of life To understand how RNA and DNA contribute to physiological processes at the molecular, cellular, and organismal levels, it is important to study RNA and DNA biochemistry and to investigate their function, regulation, and biophysical properties Modeling the Structure of DNA In this activity, students build a paper model of DNA and use their model to explore key structural features of the DNA double helix This activity can be used to complement the short film The Double Helix Students use paper nucleotides printed on card stock to build a singlestranded DNA sequence assigned byWe already have an overview video of DNA and I encourage you to watch that first but what I want to do in this video is dig a little bit deeper actually get into the molecular structure of DNA and just as a starting point let's just remind ourselves what DNA stands for all right the different parts of the word in different colors so it stands for deoxy deoxyribonucleic ribonucleic ribonucleic
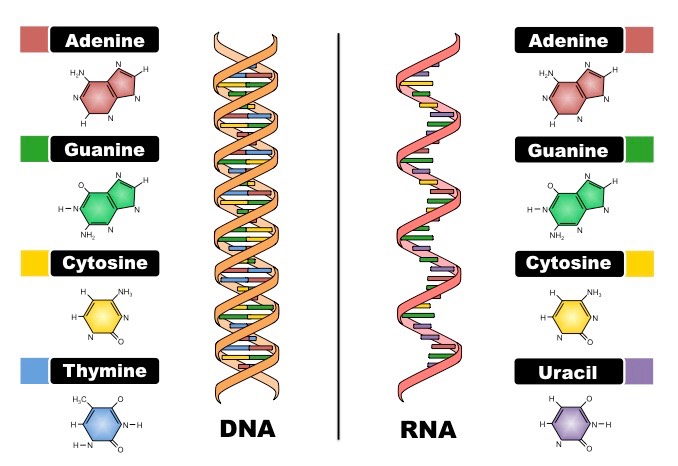
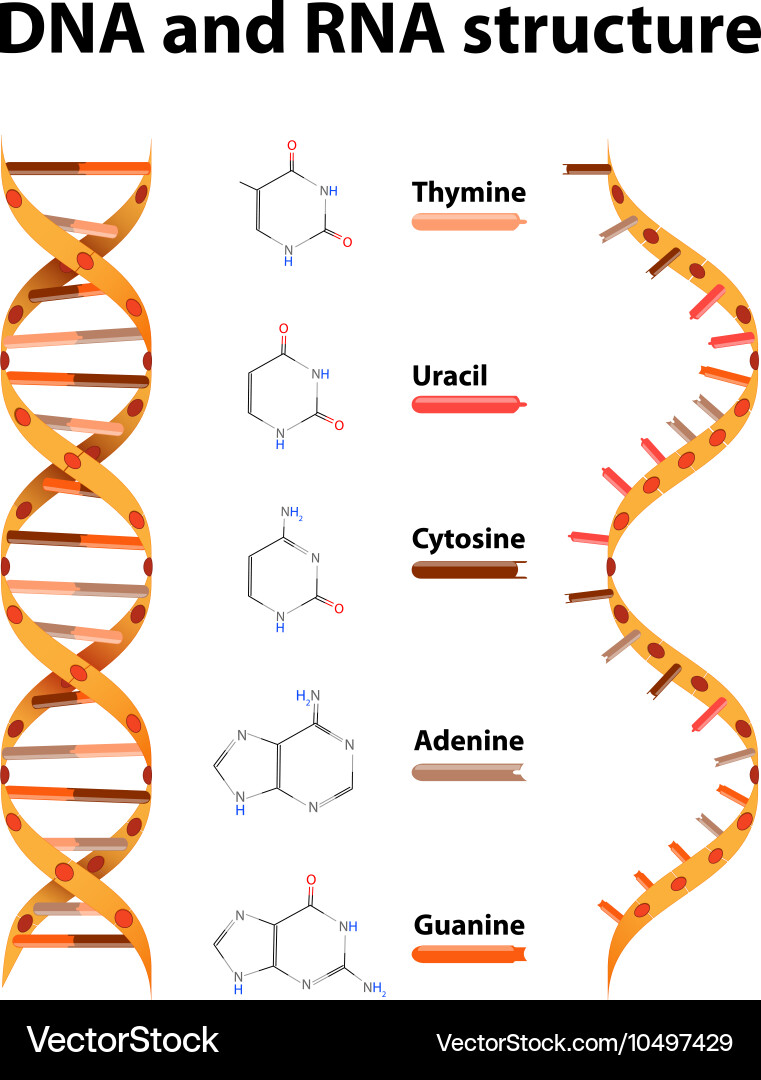
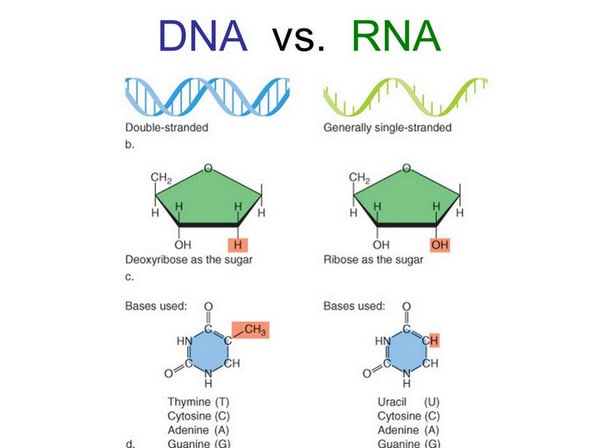
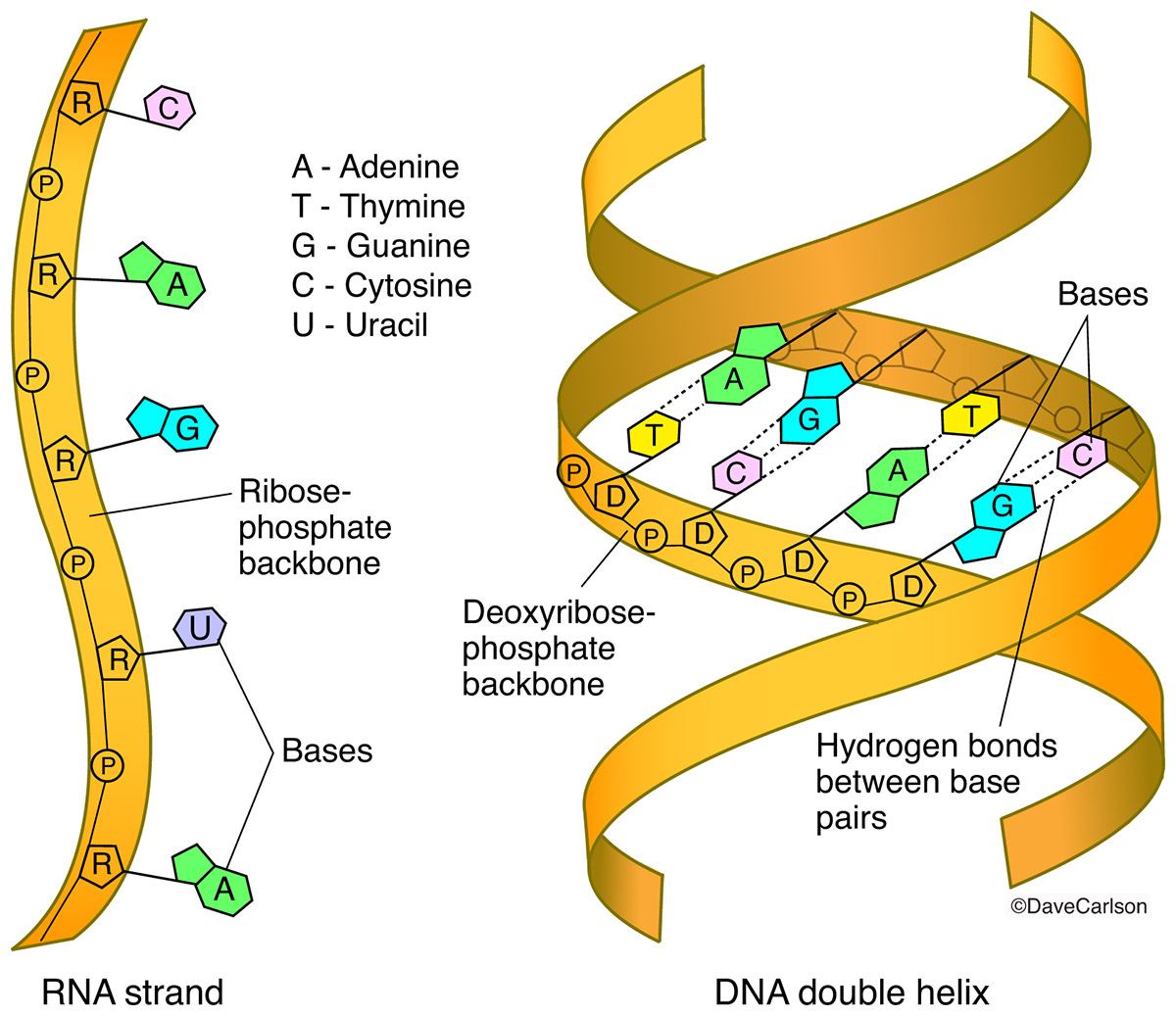
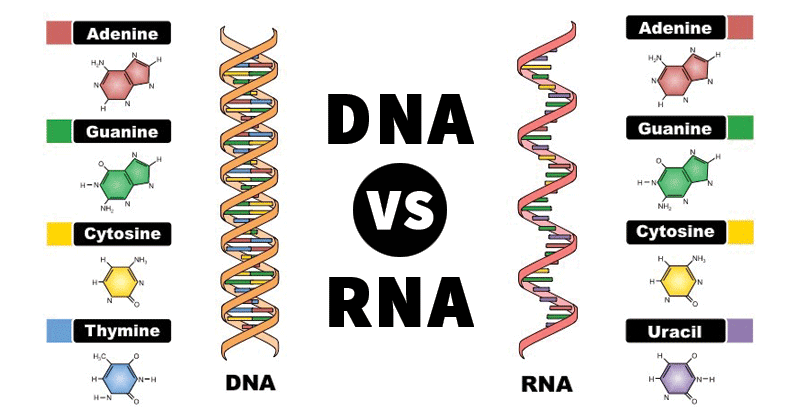
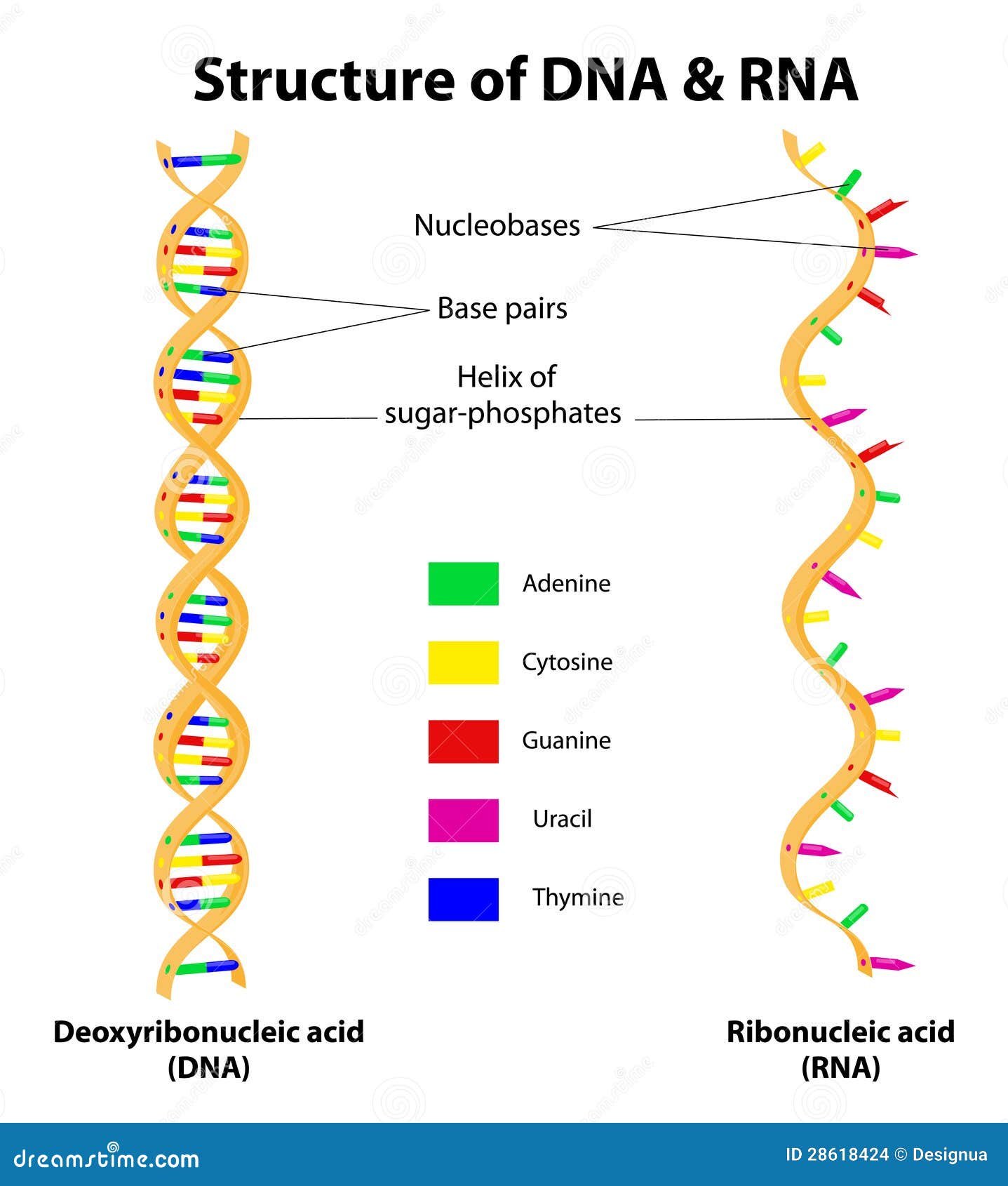
RNA is composed of a single chain or strand of nucleotides, while DNA consists of 2 separate chains or strands of nucleotide connected to one another by weak hydrogen bonds The strands of both DNA and RNA may involve very large numbers of nucleotides The DNA molecule is double stranded and it function as a ladder Please help me by listing any good software for DNA & RNA 3D structure prediction Cheminformatics Does someone know a good online tool to generate 3D DNA structure (PDB model) using as anLength In comparison, DNA is much longer than RNA A single strand of DNA would be around 2 m long RNA molecules vary in length, but they are much shorter than DNA Location DNA is located in the nucleus, with some DNA found in the mitochondria RNA forms in the nucleolus and is found in the cell's cytoplasm



Rna Secondary Structure
/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)



The Differences Between Dna And Rna
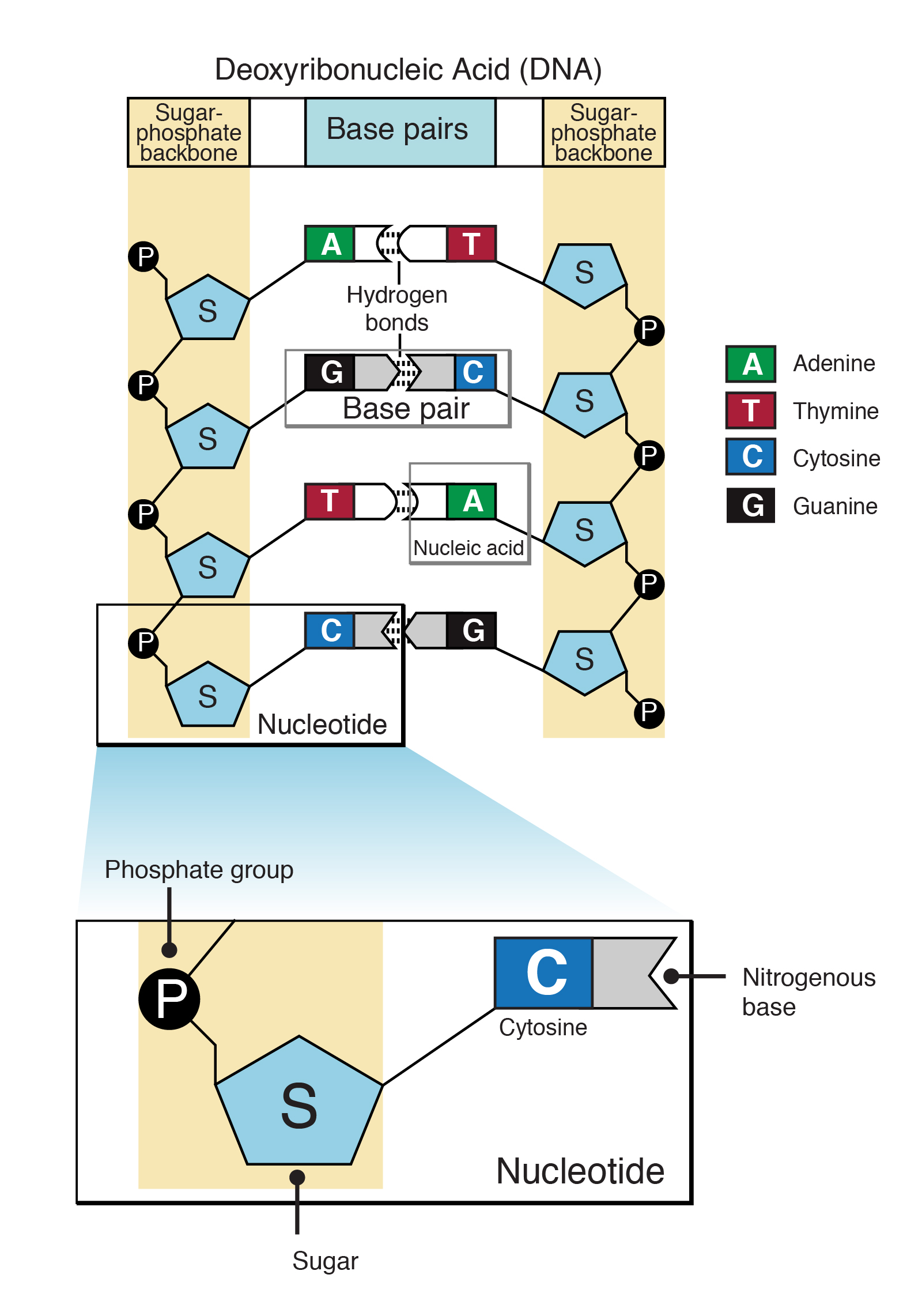
(ii) mixed DNA doublehelical structures comprised of canonical A, B, and Ctype DNA fragments;DNA carries the genetic blueprint of the cell and is passed on from parents to offspring (in the form of chromosomes) It has a doublehelical structure with the two strands running in opposite directions, connected by hydrogen bonds, and complementary to each other RNA is singlestranded and is made of a pentose sugar (ribose), a nitrogenousDNA Secondary structure is the set of interactions between bases, ie, which parts of strands are bound to each other In DNA double helix, the two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bondsThe nucleotides on one strand base pairs with the nucleotide on the other strand The secondary structure is responsible for the shape that the nucleic acid assumes



Dna And Rna Structure Royalty Free Vector Image




M2 Unit 3 G10 Dochub
Structure Of DNA & RNA By Himanshu Dev VMMC & SJH DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA a polymer of deoxyribonucleotides Usually double stranded And have doublehelix structure found in chromosomes, mitochondria and chloroplasts Helix model for the structure of DNA The key difference between DNA and RNA structure is that the DNA structure is a double helix composed of two complementary strands while RNA structure is singlestranded Nucleic acids are macromolecules or biopolymers Moreover, they are the building blocks of genetic material of an organism They are comprised of nucleotide chains linked via phosphodiesterImportance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms Their main function is to maintain and transmit the genetic code This information is stored in the form of long polymer chains Although the information they carry is onedimensional, it is essential to understand the 3D structure of nucleic



Life Sciences Cyberbridge



Nucleotide
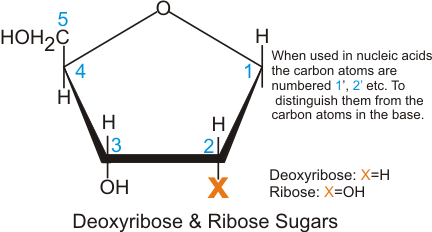
The Structure of RNA There is a second nucleic acid in all cells called ribonucleic acid, or RNA Like DNA, RNA is a polymer of nucleotides Each of the nucleotides in RNA is made up of a nitrogenous base, a fivecarbon sugar, and a phosphate group In the case of RNA, the fivecarbon sugar is ribose, not deoxyriboseThere are two types of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA Nearly all organisms use DNA, not RNA, as the central repository for genetic information Choose the statements that explain this phenomenon a DNA is flexible and forms complex catalytic structures b DNA contains a hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon c DNA has a double stranded structure thatBiological functions of RNA molecules are dependent upon sustained specific threedimensional (3D) structures of RNA, with or without the help of proteins Understanding of RNA structure is frequently based on 2D structures, which describe only the Watson–Crick (WC) base pairs Here, we hierarchically review the structural elements of RNA and how they contribute to RNA 3D



Difference Between Dna And Rna Laboratoryinfo Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotides-5c253d8cc9e77c0001d9b089.jpg)



The Differences Between Dna And Rna
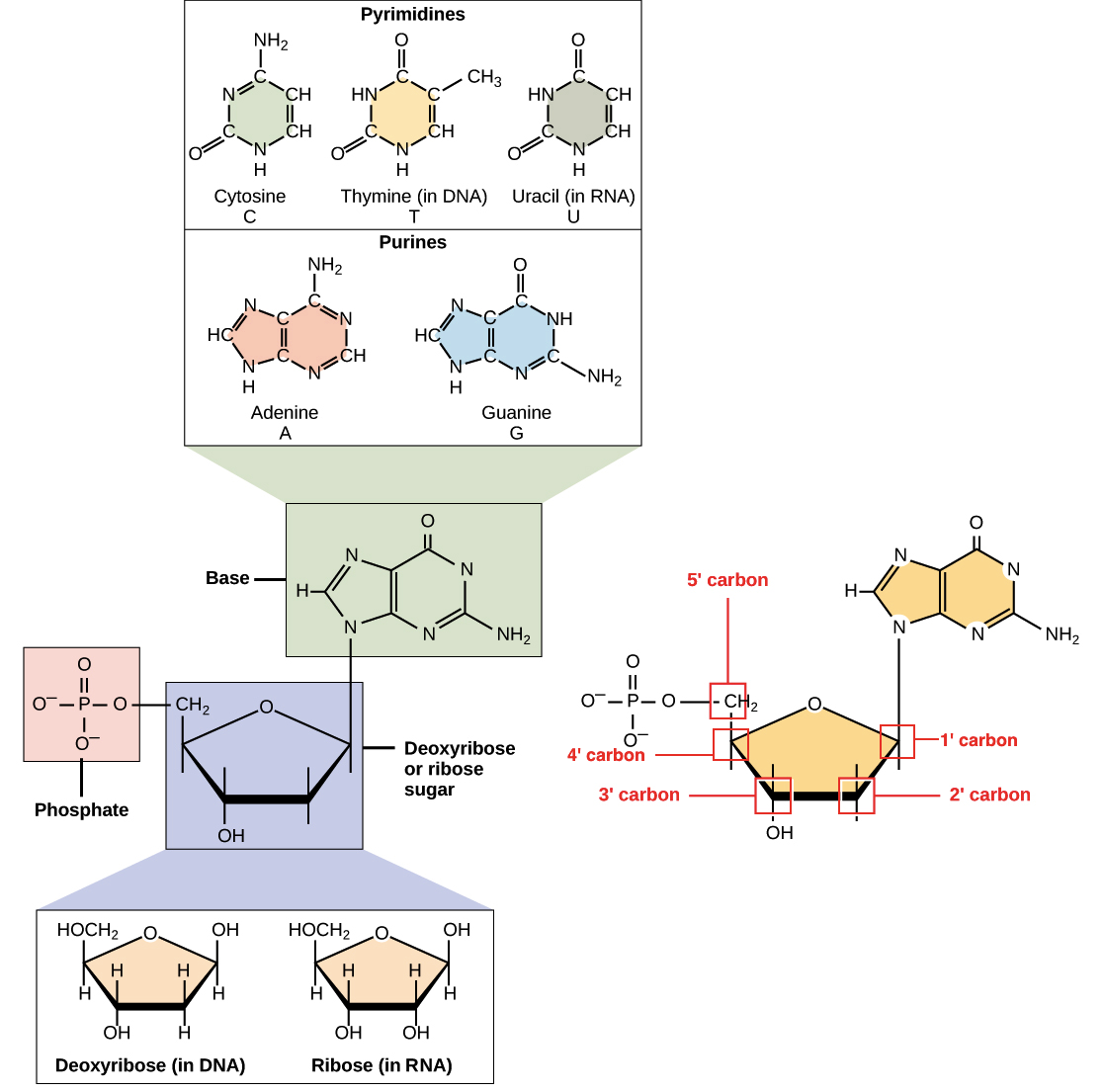
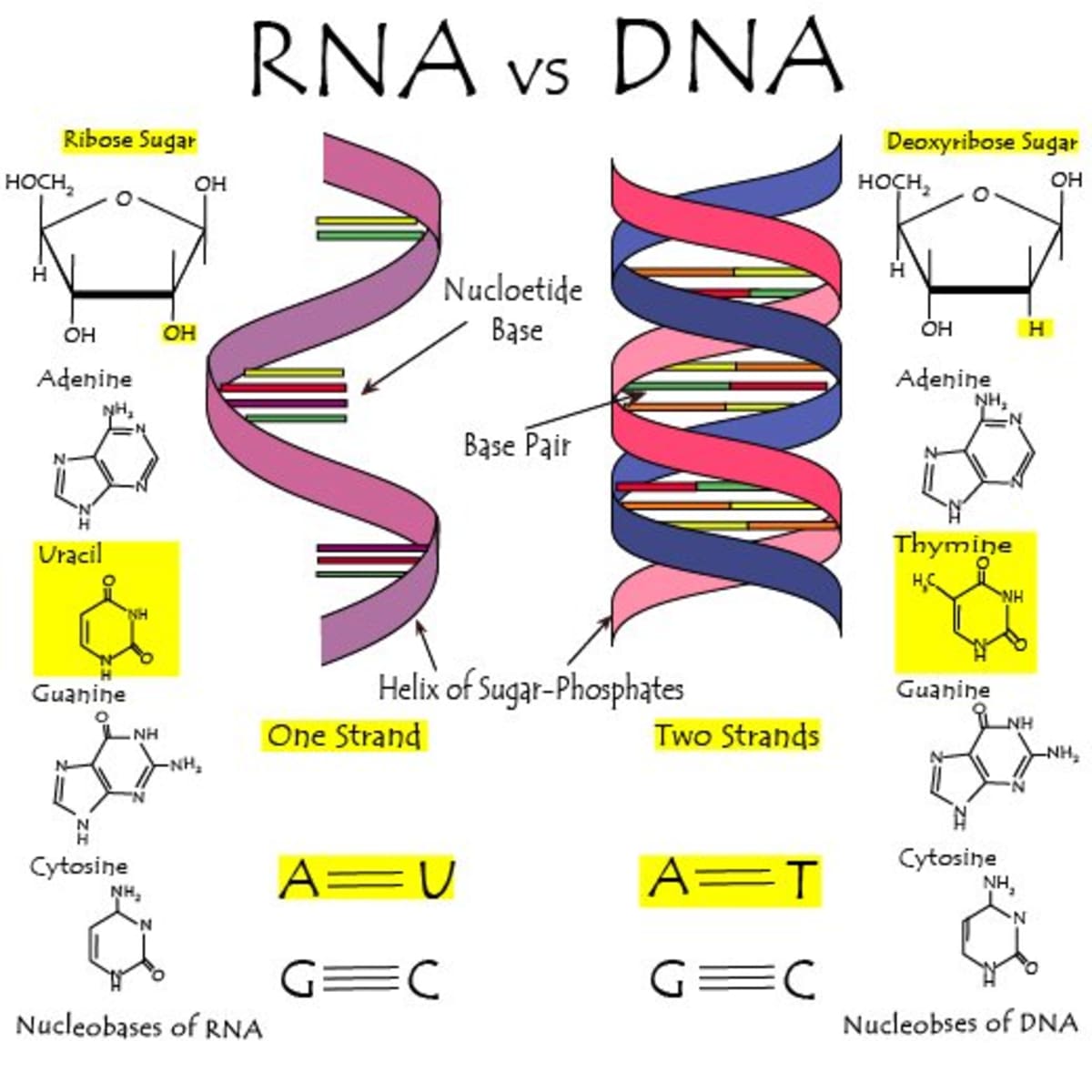
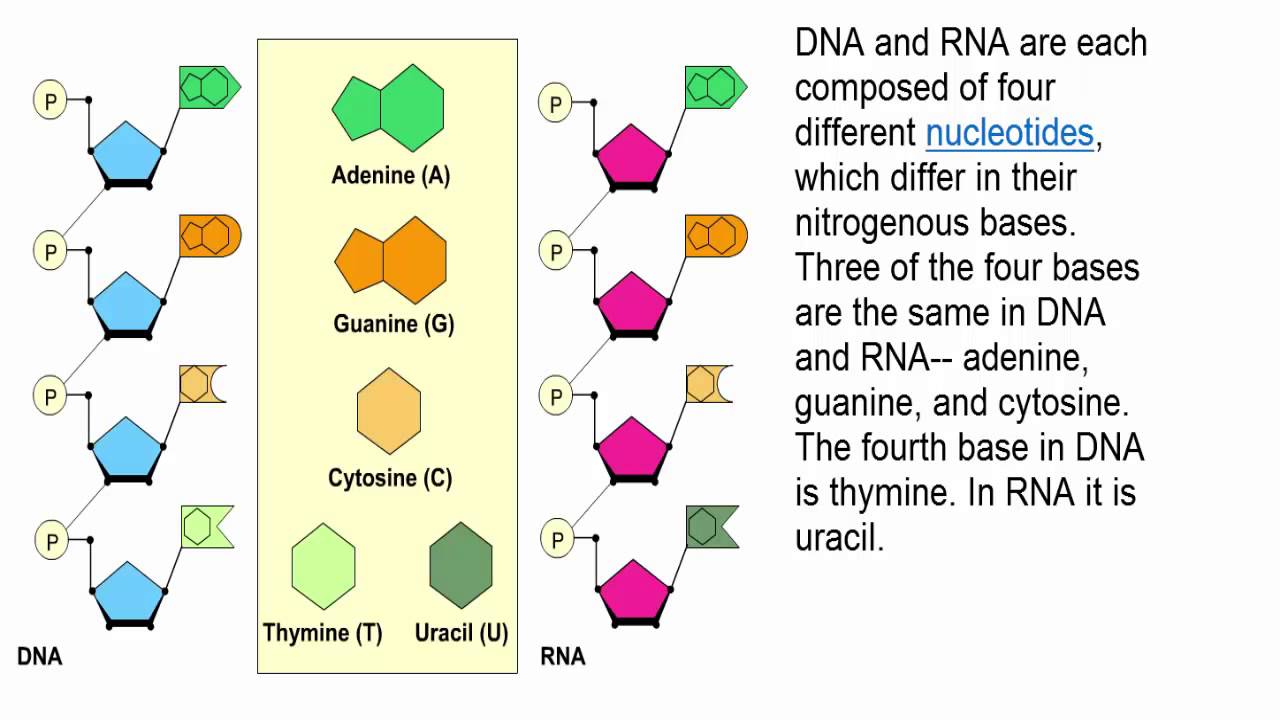
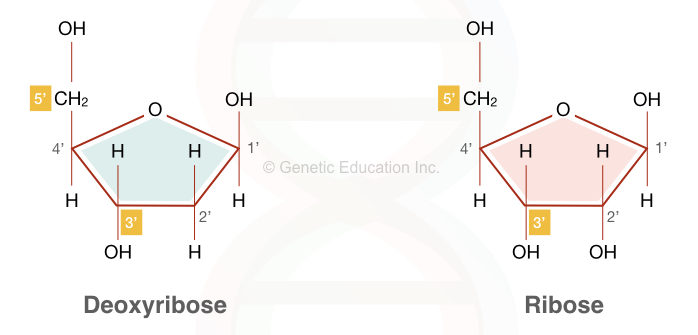
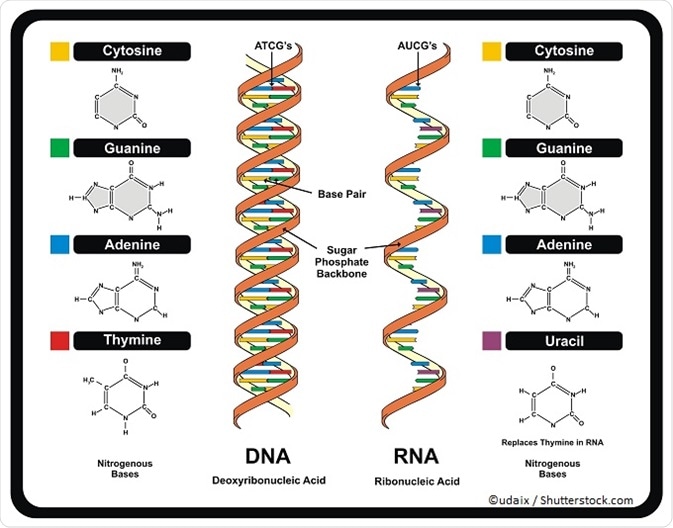
RNA pairs with DNA, G and C always pair together, T in DNA always pairs with A in RNA, but A in DNA pairs with U in RNA When RNA pairs with RNA, then G pairs with C and A pairs with U Third, RNAissinglestranded(usually)whileDNAisdoublestranded That is, RNA does not have the ladderlike structure of the DNA in Figure 31 Instead, RNA would DNA Model The threedimensional structure of DNA, first proposed by James D Watson and Francis H C Crick in 1953, consists of two long helical strands that are coiled around a common axis to form a double helix Each DNA molecule is comprised of two biopolymer strands coiling around each other Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts a deoxyribose (5carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base ( Figure 93 ) There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA



What Are The Similarities Between Dna And Rna Albert Io




Rna Structure Wide Discovery Of Functional Interactions With Multiplexed Rna Motif Library Nature Communications
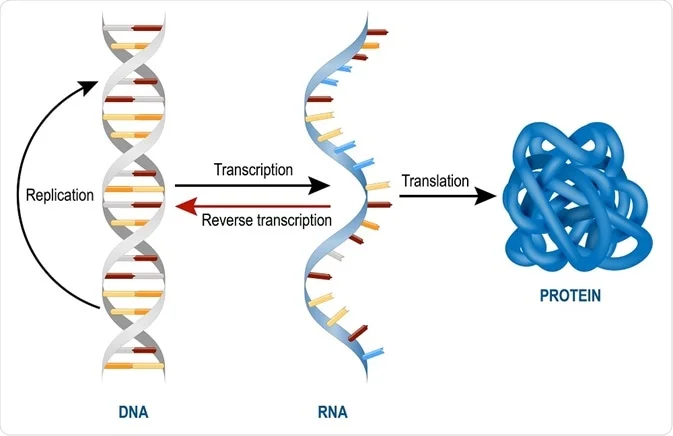
DNA, RNA, replication, translation, and transcription Overview Recall the central dogma of biology DNA (genetic information in genes) RNA (copies of genes) proteins (functional molecules) DNA structure One monomer unit = deoxyribonucleic acid • composed of a base, a sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate The nitrogenous bases include adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine RNA mostly exists in the singlestranded form, but there are special RNA viruses that are doublestranded The RNA molecule can have a variety of lengths and structures An RNA virus uses RNA instead of DNA as its genetic material and can cause many human diseasesDNA structure and function DNA is the information molecule It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes




2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Sl Hl 1 Biology 5 Ferguson



Nucleic Acids Article Khan Academy
111 DNA and RNA Structure and Function Your DNA contains the recipes for the proteins that your cells make A segment of DNA that contains the recipe for building one protein is called a gene Genes occur on chromosomes Mutations in genes can cause metabolic errors and genetic diseasesDNA and RNA are key carriers of biological information For example, DNA may store a gene coding for haemoglobin or insulin, which is then processed by RNA and ribosomes (which are sophisticated machines themselves made of RNA and proteins) to manufacture those proteins Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids (that's the "NA" part of their acronym)(iii) proteindecorated DNA structures with userdefined binding



Dna And Rna Structures



Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry
Structure of RNA The tRNA has a cloverleaf like structure It is synthesized in the nucleus on a small part of DNA In 1965, RW Holley suggested the cloverleaf model of tRNA Though tRNA molecule consists of a single strand, it assumes clover leaf like structure through folding There are three folds in the clover leaf tRNA26 Structure of DNA and RNA 26U1 The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides 26U2 DNA differs from RNA in the number of strands present, the base composition and the type of pentose 26U3 DNA is double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs The Structure Of DNA and RNA Ferdous Ahamad Opi Genetics , Lead , Physiology 3 Comments 485 Views One of the features of the 'genetic molecule' would have to be the ability to carry instructions – a sort of blueprint – for the construction and behavior of cells and the way in which they grow together to form a complete living organism




Nucleic Acid Secondary Structure Wikipedia




0814 Structure Dna And Rna Molecule Medical Images For Powerpoint Powerpoint Presentation Slides Ppt Slides Graphics Sample Ppt Files Template Slide
RNA Structure and Function Ribonucleic acid (RNA) also consists of nucleotides, but these nucleotides contain the sugar ribose RNA has A,C,G and U Although both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, there are key differences in the structure and function of RNA and DNA There are three types of RNA and each is involved in protein synthesisStart studying DNA and RNA Structure Quiz Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsDNA AND IT' S STRUCTURE, FUNCTION, TYPES, MODES OF the "NA" in DNA (deoxyribonucleicacid) and RNA (ribonucleicacid) Two years earlier, the Czech monk Gregor Mendel, The second aspect is very significant as the accepted DNA model should be such that it explains biochemically the various aspects




Rna Double Helix Structure Identified Using Synchrotron Newsroom Mcgill University
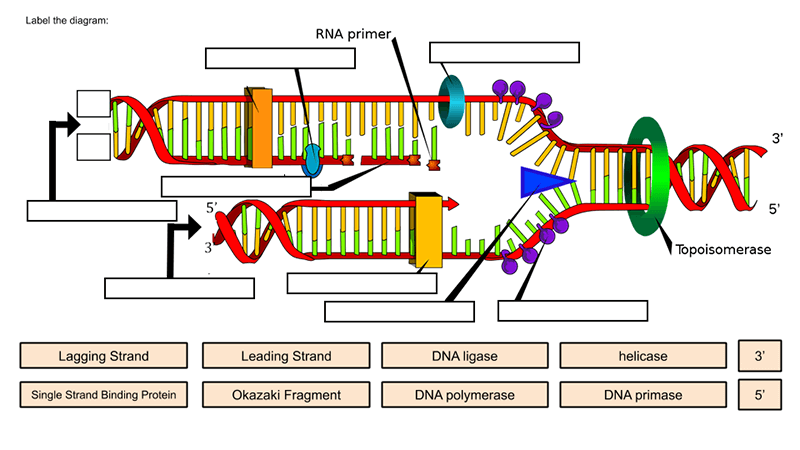



Dna Drag And Drop
Watson and Crick model of DNA provides one of the best ways to demonstrate the structure of doublehelix DNAA DNA is a polymer composed by the combination of several monomer units (deoxyribonucleotides) linked by the phosphodiester bondIn the discovery of DNA, many scientists have contextualized the structure of DNA, its components and composition etcThe chemical structure of RNA is very similar to that of DNA, but differs in three primary ways Unlike doublestranded DNA, RNA is a singlestranded molecule in many of its biological roles and consists of much shorter chains of nucleotides However, a single RNA molecule can, by complementary base pairing, form intrastrand double helixes, as in tRNA Structure of dna and rna 1 Structure Of DNA & RNA By Himanshu Dev VMMC & SJH 2 DNA 3 DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA a polymer of deoxyribonucleotides Usually double stranded And have doublehelix structure found in chromosomes, mitochondria and chloroplasts It acts as the genetic material in most of the organisms Carries the genetic




Dna Structure Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



1
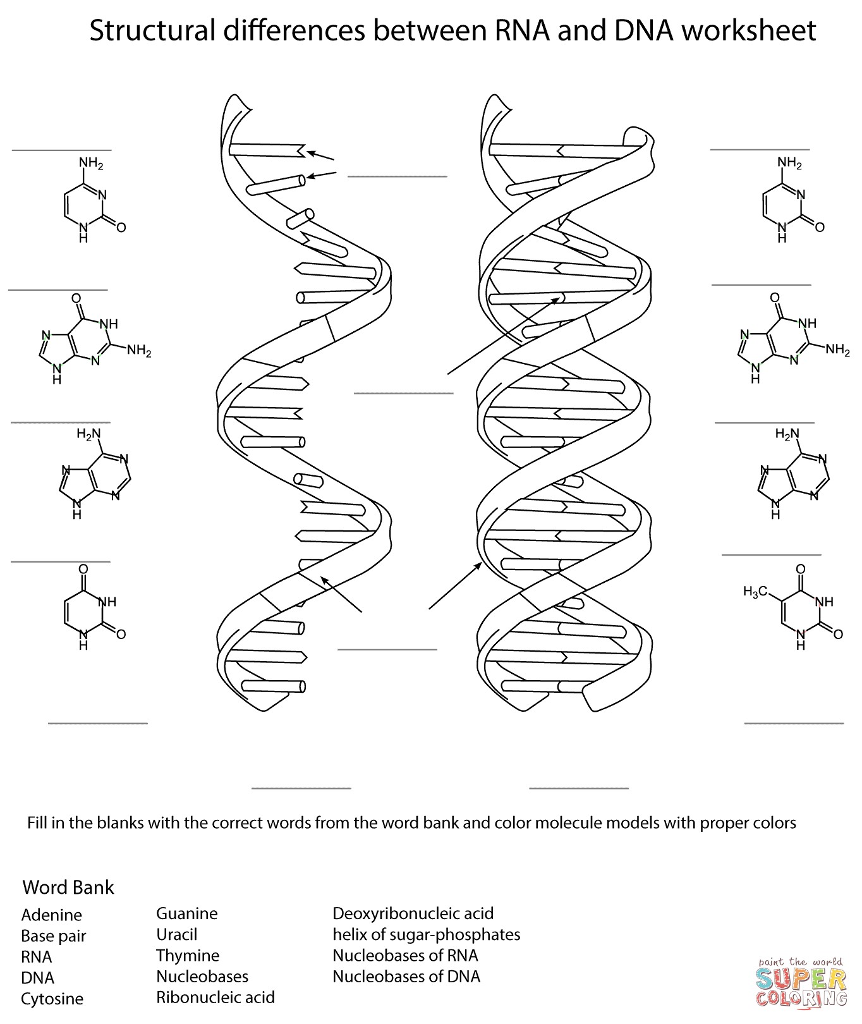



Solved Structural Differences Between Rna And Dna Worksheet Chegg Com
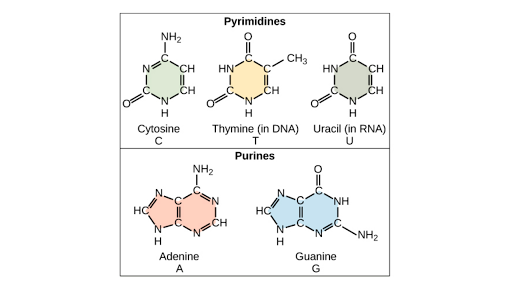



Nucleic Acids Article Khan Academy
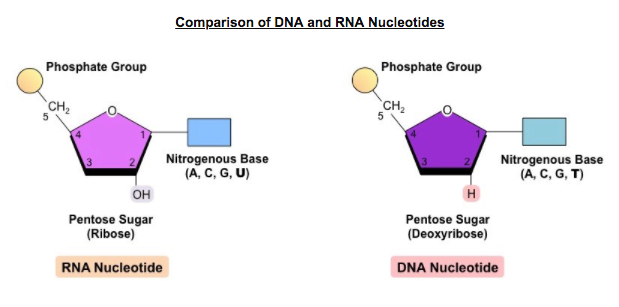



2 6 Dna Rna Structure




Dna Model Learning About Dna Structure Function And Replication




Nucleic Acids Dna And Rna Structure Youtube
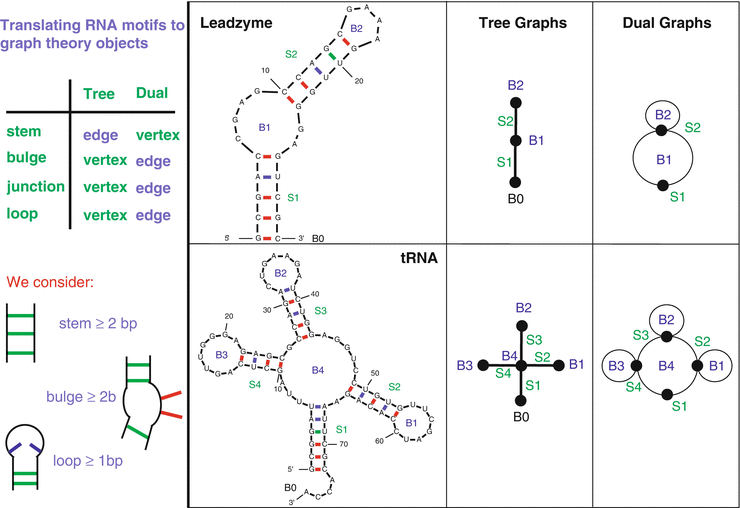



Rna Structure Analysis And Design Graph Theory Springerlink



Structure Of Dna And Rna



Structure Of Dna And Rna



Lecture 10 Nucleic Acids Dna Rna Types Of



Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii



Rna World Wikipedia




Dna Vs Rna Biology Dictionary




Dna And Rna Structure Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock



Dna Rna Structure Carlson Stock Art



The Differences Between Dna And Rna Explained With Diagrams Owlcation



Rna Structure And Function
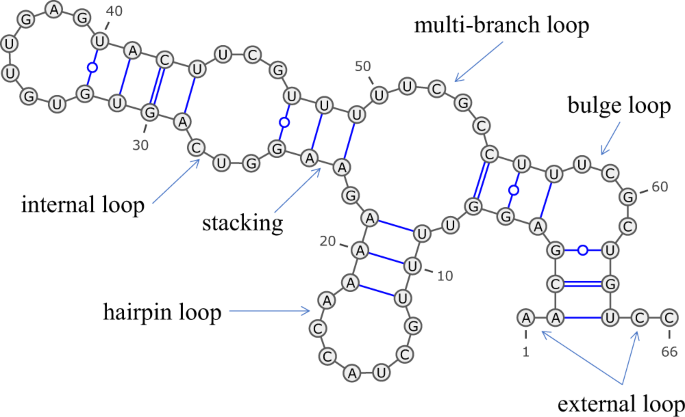



Rna Secondary Structure Prediction Using Deep Learning With Thermodynamic Integration Nature Communications




Dna And Rna Structure And Function Youtube
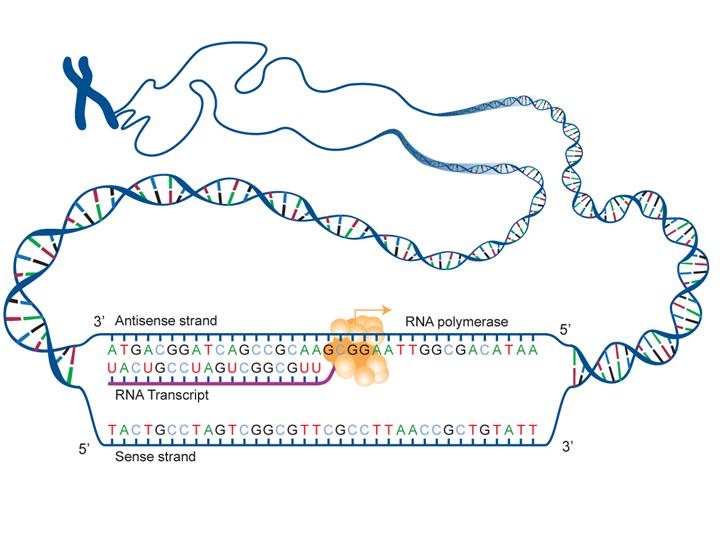



Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network
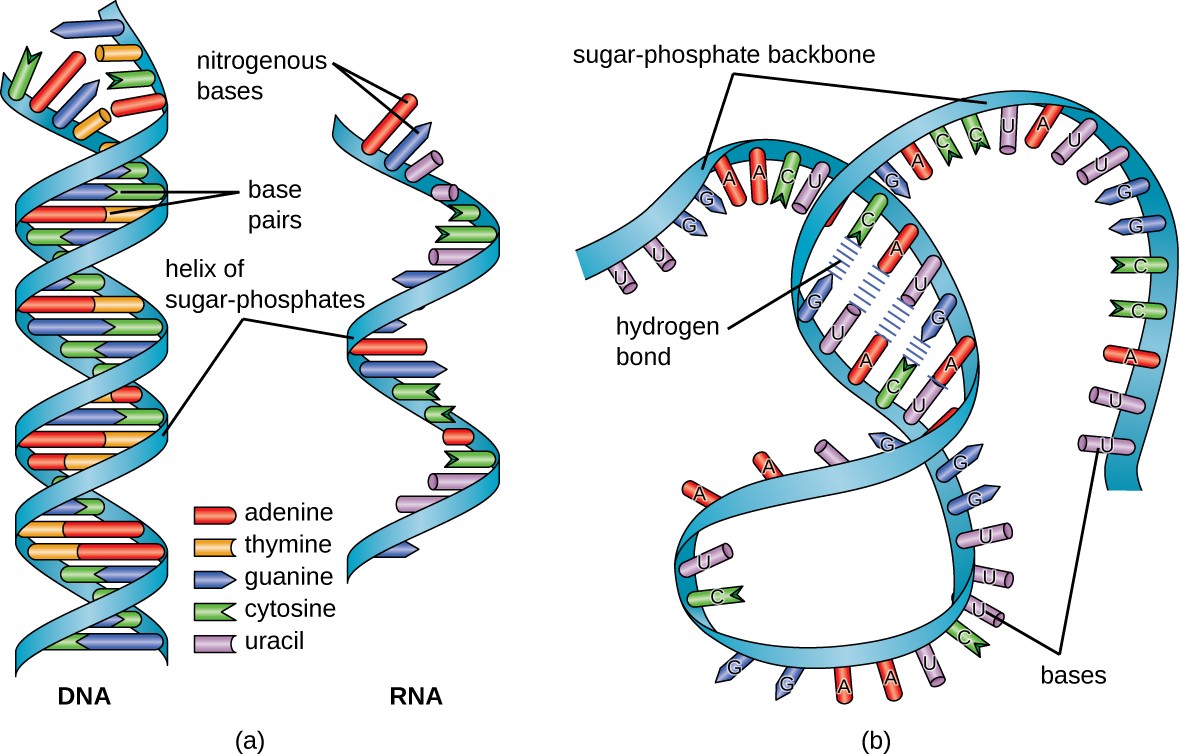



Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology



Nucleotide
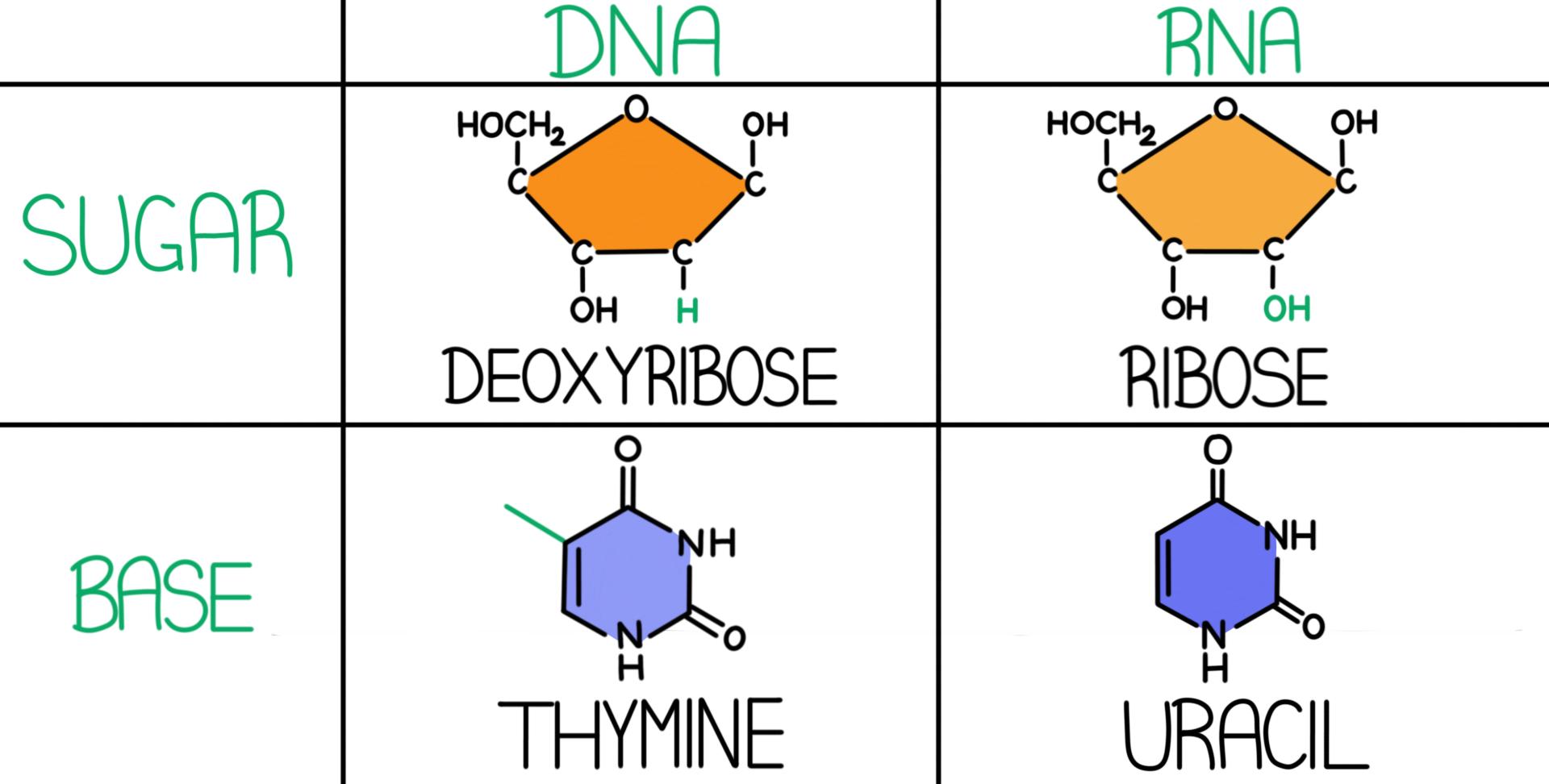



Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii




Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii




Dynamic Dna Kit C




What Are The Monomers Of Dna And Rna Study Com




Dna Vs Rna Differences And Similarities



Rna Dna Secondary Structure Fold Viewer




Structure Of Rna And Dna Illustration Stock Image C028 8010 Science Photo Library



Dna And Rna Structure Youtube




Make A Candy Dna Model Stem Activity




Modeling Dna And Rna Structure With Gummy Bears Iteachly Com



Differences Between Dna And Rna Vector Scientific Icon Spiral Of Dna And Rna An Illustration Of The Differences In The Structure Of The Dna And Rna Stock Vector Image Art



30 Differences Between Dna And Rna Dna Vs Rna



Types Of Rna Mrna Rrna And Trna




Scientific Model Dna And Rna Transcription And Translation Vector Isolated On White Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock



Watson And Crick Dna Model Molecular Biology Microbe Notes



Dna Vs Rna Differences And Similarities



Nucleic Acid Structure Wikipedia



File Difference Dna Rna En Bw Svg Wikimedia Commons



Structure Dna And Rna Molecule Vector Stock Vector Illustration Of Human Education




What Are The Similarities Between Dna And Rna Albert Io




The Chemical Structure Of Dna Compound Interest



Dna Rna Structure Model India Manufacturers Suppliers Exporters In India




What Are The Structure Of Rna And Dna And How One Might Be Used To Create The Other Socratic




Structure Of Nucleic Acids Structure Of Dna Structure Of Rna Dna Structure And Rna Structure Youtube



Rcsb Pdb 1ac3 Solution Structure Of An Rna Dna Hybrid Duplex Containing A 3 Thioformacetal Linker And An Rna A Tract Nmr 8 Structures




Differences Between Rna And Dna Types Of Rna Mrna Trna Rrna Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
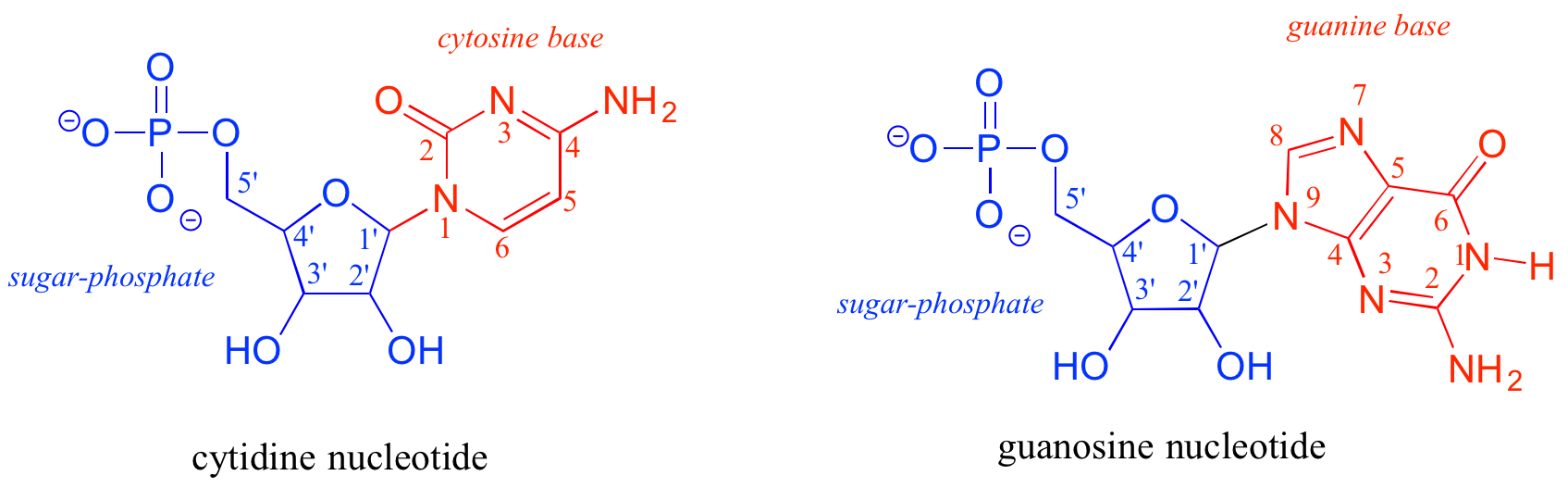



1 4 4 Introduction To Nucleic Acid Dna And Rna Structure Chemistry Libretexts
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=627&height=436)



1 2 Structure Of Dna And Rna Biology Libretexts



Structure Of Dna And Rna




Double Helix Structure Of Dna Or Rna And Its Components Nucleotides Download Scientific Diagram




Computer Modeling Of Three Dimensional Structure Of Dna Packaging Rna Prna Monomer Dimer And Hexamer Of Phi29 Dna Packaging Motor Journal Of Biological Chemistry



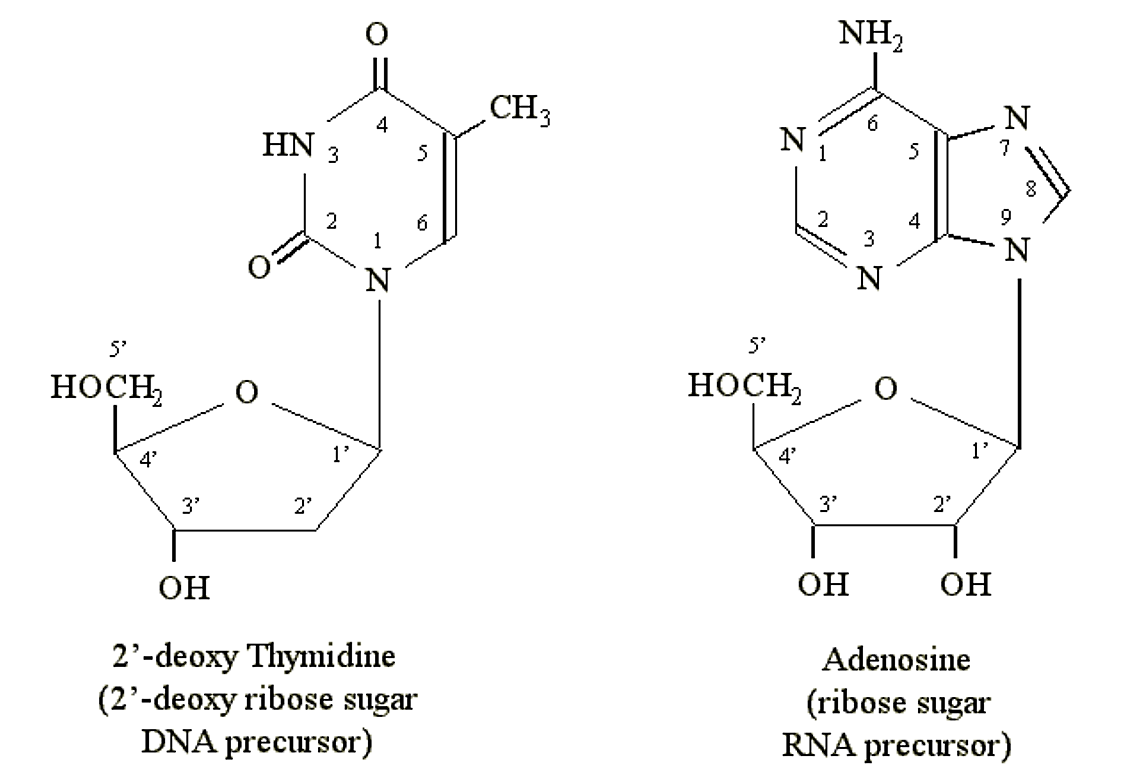
Structure Of Dna And Rna
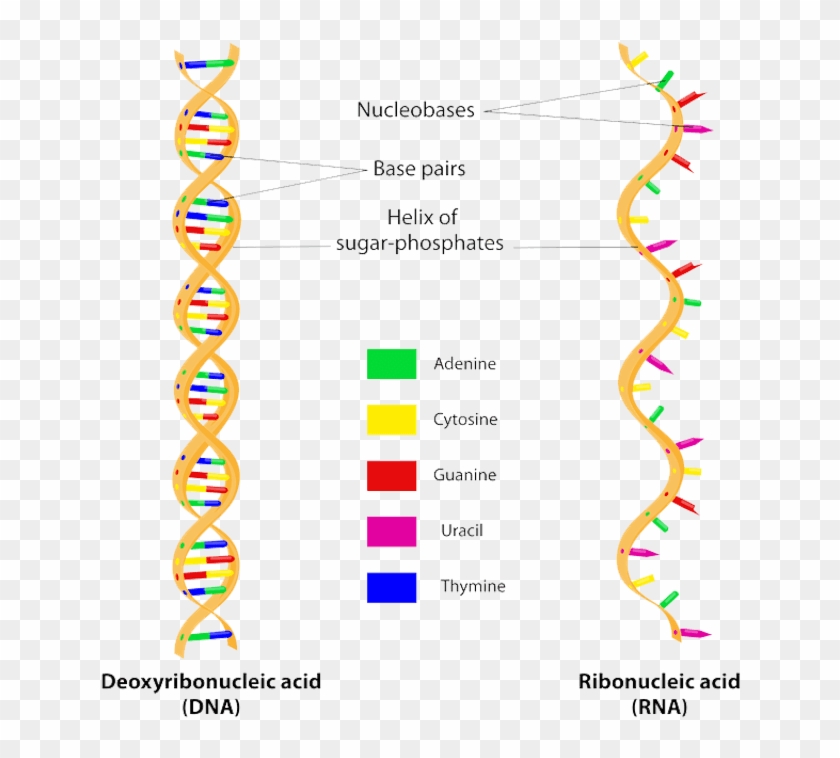



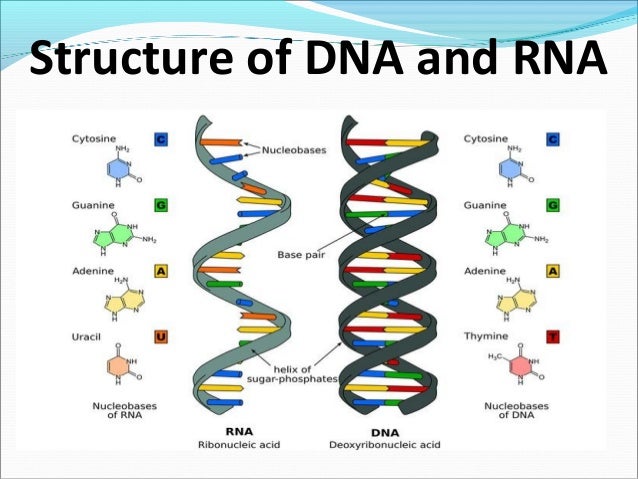
About The Mcat Structure Of Dna Rna Hd Png Download 700x718 Pngfind



Dna Structure
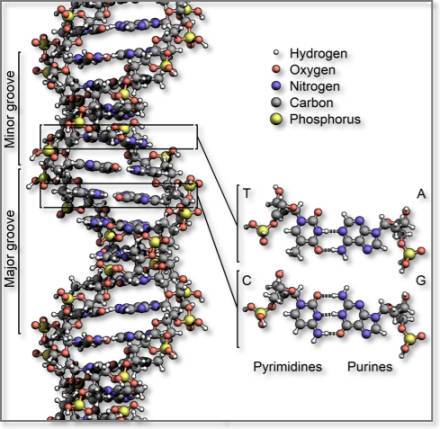



Dna And Rna Computational Medicine Center At Thomas Jefferson University




Ribose And Deoxyribose Molecular Structures Dna And Rna Components 3d Model Ball And Stick Style Vector Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks




Structure Of Dna Rna And Arabinonucleic Acids Ana Download Scientific Diagram




Dna Rna 3d Model



3
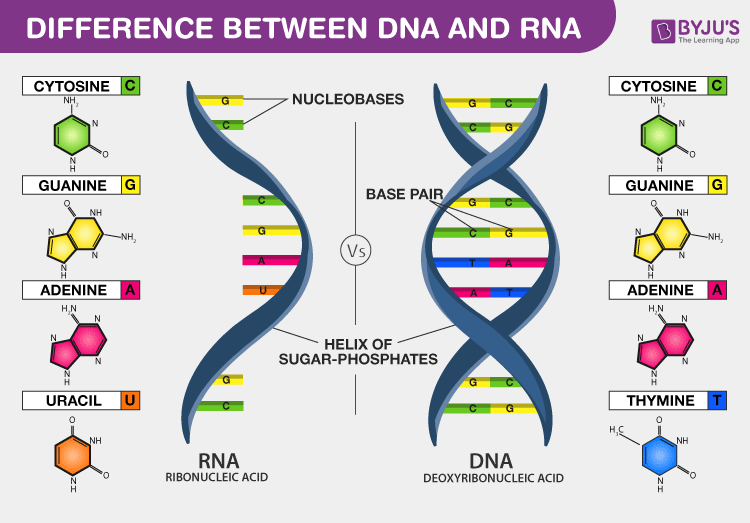



Dna Vs Rna Introduction And Differences Between Dna And Rna




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks




Dna Vs Rna Difference And Comparison Diffen
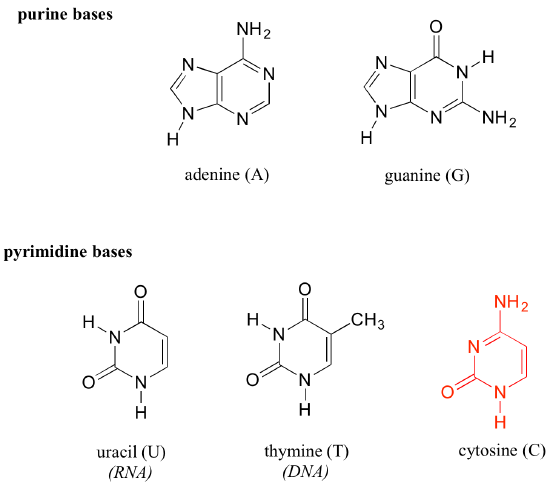



1 4 4 Introduction To Nucleic Acid Dna And Rna Structure Chemistry Libretexts




Dna Versus Rna Bioninja
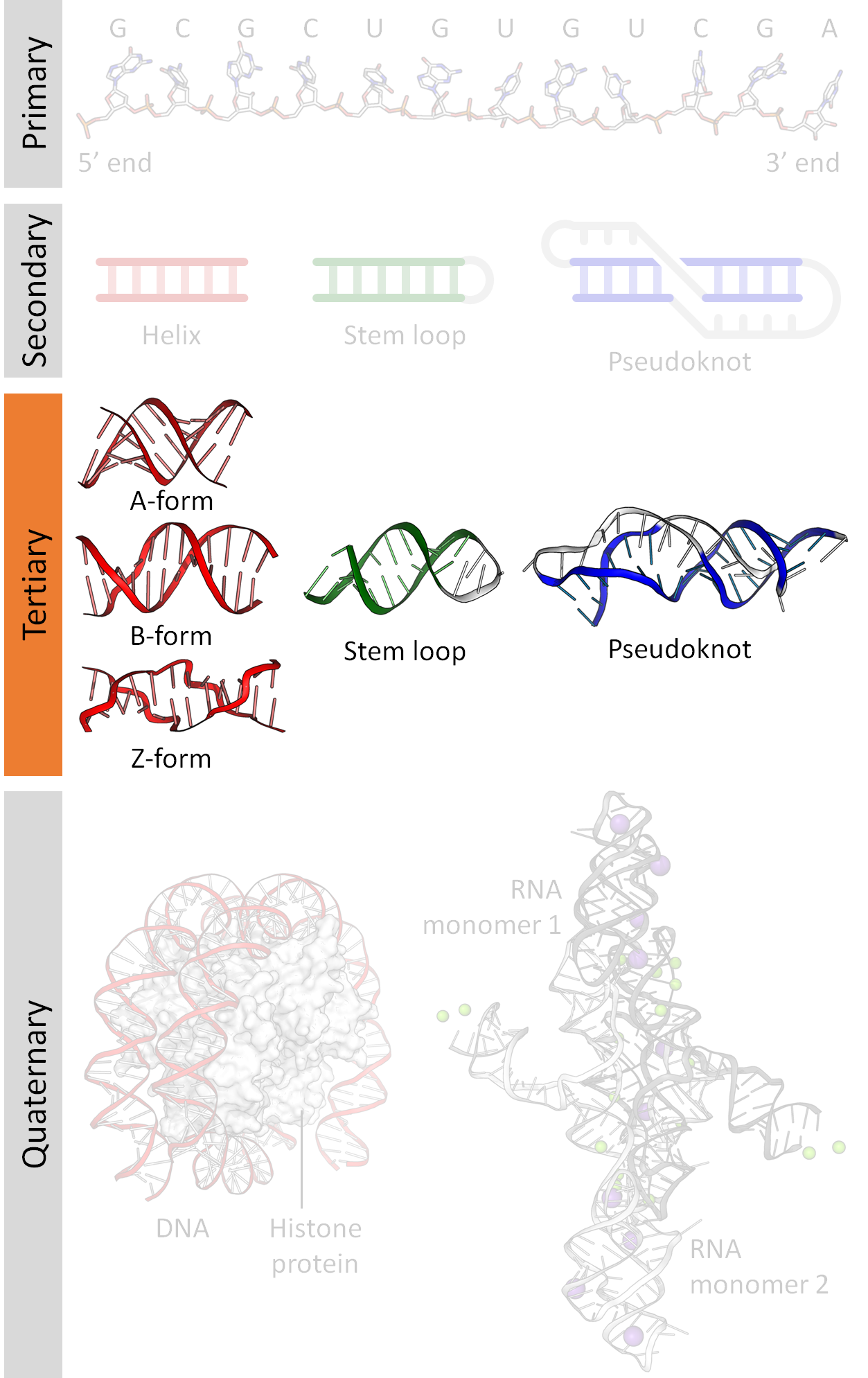



Nucleic Acid Tertiary Structure Wikipedia



Structure Of Dna And Rna




Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica
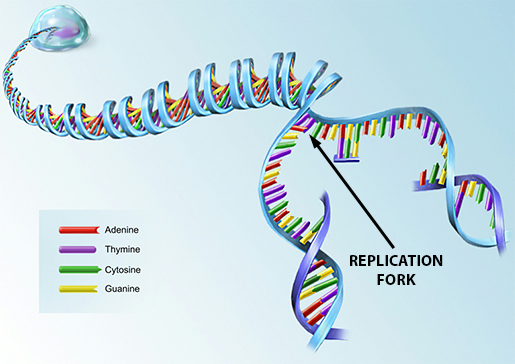



Dna And Rna Basics Replication Transcription And Translation



2




Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology



What Is The Rna World Hypothesis




Using Dna Rna To Model The Structure Of Photon And Neutrino Physics Focus Series Book 6 By Archimedes Plutonium




Dna Model Project Worksheets Teachers Pay Teachers



Pdf The Structures Of Dna And Rna



Module 1 Part C Dna Structure And Function Genetic Engineering And Cancer
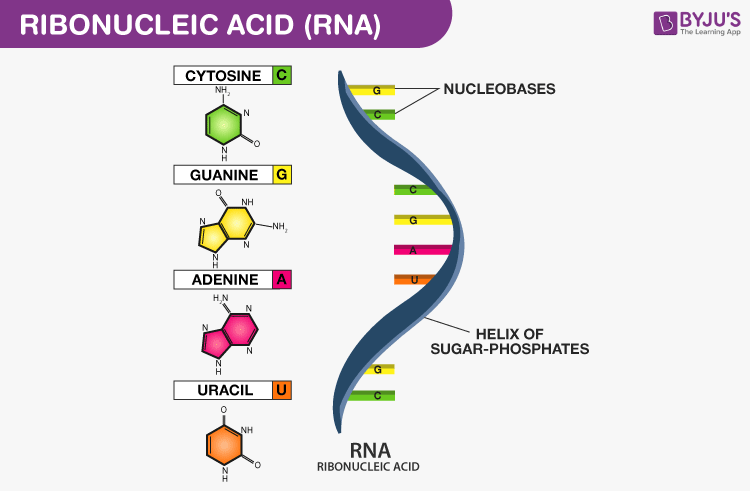



Rna Structure Functions And Types Of Rna




Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica




Unit 4 Concept 1 Dna And Rna Structure Diagram Quizlet




Dna Vs Rna Biology Dictionary
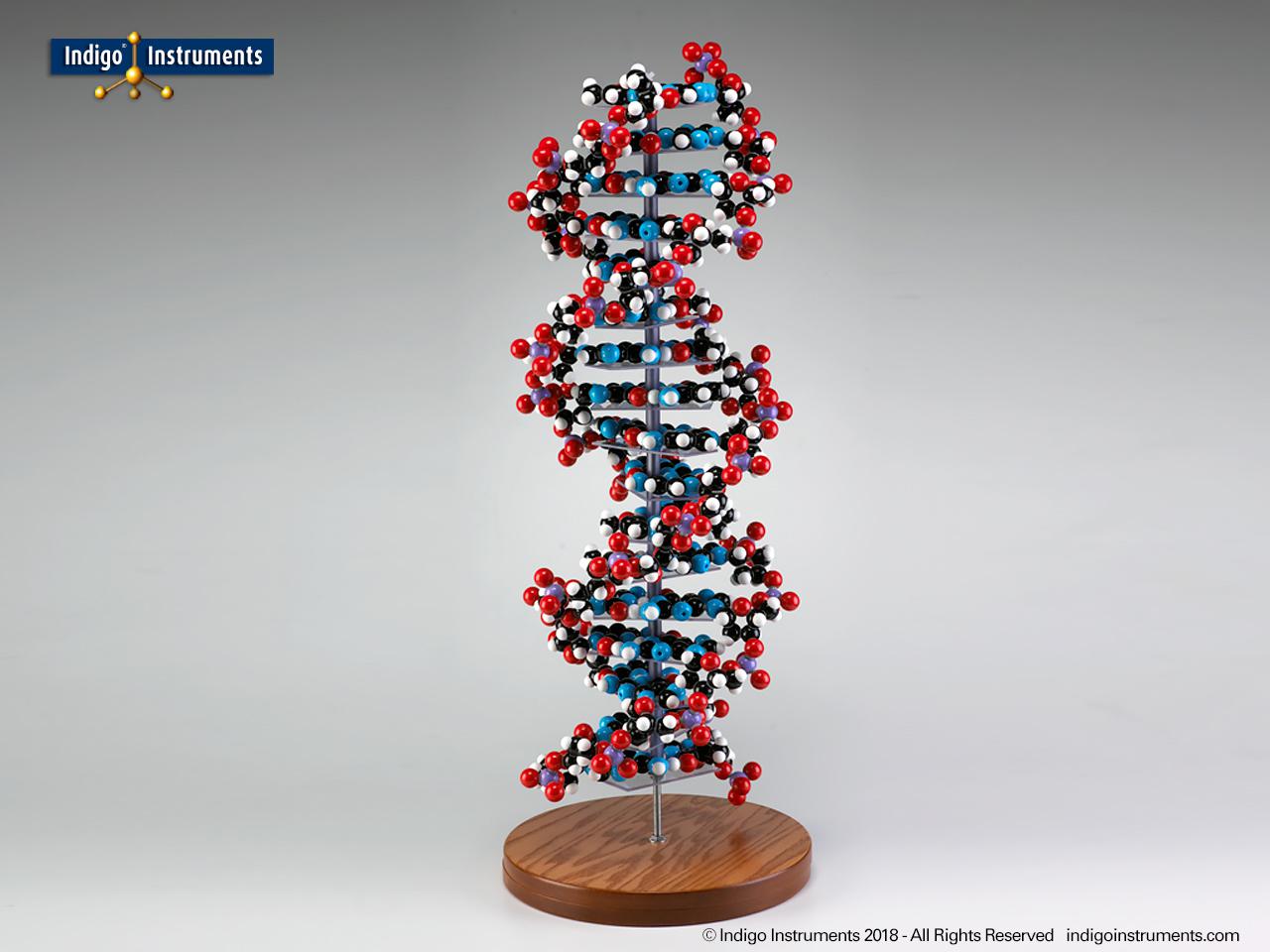




Dna Double Helical Structure Models 12 17 22 36 Bases From Indigo



Blender Dna Rna And Extreme Backward Compatibility Blendernation




Amazon Com 3b Scientific W Dna Rna Model 50cm Height Industrial Scientific



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿